Both horses and riders can carry a lot of fear that blocks the joy they could be having together. Traumatic experiences can set everyone back and rightfully so. We all go into protective mode when something bad happens. Sometimes we lose confidence, in our bodies, in the world around us, and in our horses.

When I was teaching a lot of liberty work clinics, many of the people who attended had either been bullied into being pushy with their horses by trainers, or they had gotten hurt by horses. When either of those or both of those things happen, a natural reaction is to draw into oneself and find something else to do; perhaps some other way to be with horses that’s not so stressful, or put them in the pasture and leave them, saying that horses don’t need to be ridden, they’re totally happy having minimal interaction with humans. That’s all fine and true to some extent, but there is so much that is not being addressed here. It may allow the person to remain in their comfort zone or create an even narrower one, in order to accommodate their fears. And the fact they can provide a pasture and freedom is huge and wonderful! But it doesn’t develop the relationship with the horse, and it doesn’t develop the part of themselves that can really listen to the horse. Bottom line – it is all fear-based, as is bullying types of training.
While working with horses, I must be conscious of so much around me, like on every plane and in every dimension. Even with all that consciousness, something may enter my zone or my horse’s zone and upset the apple cart.
We all know that – you have your horse “de-sensitized” to large trucks, bicycles, etc. but what about that odd machine that comes down the railroad tracks that makes a strange noise? Or the new silent electric bikes that make some noise that bothers some horses? The horse may be fine with some stimuli but really worried about others.
If you stay in the arena, you may not need to experience any of these things. But horses react to things happening in or around arenas too.
 A cumulative event that happens to horses and humans is trigger stacking. One bad accident occurs, or one trainer mistreats the horse, but then another insult occurs. The frightened horse falls into a ditch on the trail. The frightened horse is forced to do something he’s terrified of, and it goes on like this, until he has a build up of tension under the hood so he becomes reactive to many more things than what started it. Horses who have endured repeated trauma may freeze, shut down or explode, the same responses that humans experience when they are the victims of repeated trauma. They may do a combination of these things. Horses may seem “bomb-proof” to some people because they’re shut down, but if you take them out of whatever ”comfort zone” they have, they may explode. This is because they are living in their sympathetic nervous system, their “flight/fright/freeze” mode. We want to embody treatment and exercises that bring the horse into the parasympathetic nervous system, the “rest and relaxation” mode.
A cumulative event that happens to horses and humans is trigger stacking. One bad accident occurs, or one trainer mistreats the horse, but then another insult occurs. The frightened horse falls into a ditch on the trail. The frightened horse is forced to do something he’s terrified of, and it goes on like this, until he has a build up of tension under the hood so he becomes reactive to many more things than what started it. Horses who have endured repeated trauma may freeze, shut down or explode, the same responses that humans experience when they are the victims of repeated trauma. They may do a combination of these things. Horses may seem “bomb-proof” to some people because they’re shut down, but if you take them out of whatever ”comfort zone” they have, they may explode. This is because they are living in their sympathetic nervous system, their “flight/fright/freeze” mode. We want to embody treatment and exercises that bring the horse into the parasympathetic nervous system, the “rest and relaxation” mode.
I work with a gelding who has had some rough handling in his early years, and then spent years with relatively no training, rand highly reactive to noise, vibration, sudden movements: you name it. A lot had to change for him, which it did, in the form of a wonderful, quiet new owner and some slow, considerate training. We’re still working to defuse those stressful responses because, while he has worked through a lot, he was a victim of trigger stacking in his early years.
 Bodywork – Bodywork was not always something this boy could tolerate, so it was done from a distance until I could get close, and until he got his special person. Fortunately, she was studying to become a bodyworker, which helped him immensely.
Bodywork – Bodywork was not always something this boy could tolerate, so it was done from a distance until I could get close, and until he got his special person. Fortunately, she was studying to become a bodyworker, which helped him immensely.
Liberty exercise and ground exercise – These activities have helped this horse’s state of mind immensely, before riding and even now, while he is a riding horse. A horse started with a frayed sense of worth needs this quiet building to bring him back to himself, to feel proud of himself. Horses can be happy with this form of interaction and so can people, because there is such rich communication available.
Riding – If the horse in question is able to be ridden, the process may be slow, but it should always be rewarding for the horse and human. Not pushing, rushing, or otherwise expecting something he isn’t able to give yet. At the same time, it’s still essential in all the work to create boundaries; no pulling or stepping on you, etc.
As there is so much cruel, hurried training or lack of training in the world of horses, more horses are coming to us with more trauma. A common method of training and part of some de-sensitizing, especially for non-compliant individuals, is to flood the horse’s space with scary objects, behaviors, sudden movements, which can completely overload the nervous system. Horses who twitch a lot or shy at a lot of things may have had this beginning. These horses need to be restarted in a quiet way, without the flooding or harsh treatment, and slow introduction to new things. It’s helpful to see what the new start exposes in terms of behaviors and fears.
Nearly every horse I work with currently has some level of trauma, or has worked through a lump of it. My rescue mare came to me some years ago carrying a lot of trauma, that was lodged in various cells in her body. She was enjoying her groundwork training and the people who were kind to her at the time, but there was an emotional sludge stuck here and there.
Once I could work with her each day, we could unravel it more effectively. I have worked with other horses who have had worse emotional sludge, and depending upon the facility of the owners, bodyworkers and trainers, they have been able to release it. I use a combination of bodywork and ground exercises to bring this about. Trauma is always part of the body, but the healing takes place only when we are able to stop reacting to it. I say reacting, because we will always respond, but it doesn’t have to be reaction. For most, it’s a series of gentle shifts, for some, it takes a lifetime. While we worked, the various triggers emerged and subsided and were no longer something she had to fixate on. As she goes through life, she will not be reactive unless provoked, she will remain calm and curious in her surroundings – as long as she has proper support.
And what does that support look like? Perhaps the most important thing that must be nurtured is mutual trust. When the horse sees her person as someone she can trust, then the nervous system can move from the high anxiety sympathetic nervous system into what we call the parasympathetic mode.
How do we develop this trust?
One way is to always be a protector to your horse. When you have your horse’s back, then your horse will have yours. He knows he can trust you.
I believe horses know what we’re saying, perhaps not the words themselves, but the intention behind them. Some people have horses all their lives and never know how to build trust with them, as long as they can ride and get where they want to go. I consider that to be a major disconnect, a disservice to the animal, and a joy the owner is missing out on.
For those who are starting out with horses, the problem is often the same, as so many riding establishments have a disconnected view. Students learn the disconnect and feel guilty for having sensitive feelings about horses, for becoming fearful because they can’t feel safe, for not having the opportunity to develop trust as well as necessary boundaries.
I assess how well horse and human are doing with this by
- Checking in with dimensions – our front/back, side/side, up/down dimensions.
- How well does the horse recover from a scary event, i.e., a plastic tarp blowing, a fall, trailer accident? How well does the person recover, i.e., continue to recount the scary incident, unable to move forward, etc.? Some things take longer than others to recover from.
- How well does the horse embrace gentle work, i.e. bodywork, groundwork?
So we come full circle to the fear that began this article – a fear that has every right to be there, but that doesn’t have to stay and burrow down and remain the basis for the way people interact with horses. Like everything good in life, it takes the time it takes to build the trust, unplug the trigger stacking and subsequent reactions, and move everybody involved to authentic, thoughtful responses and safety.





 years, I bought horses that could do what I was doing, endurance riding, though the first one was chosen because I just fell in love with her. I knew her and had been riding her for a year. Then we got into endurance riding. Even though she wasn’t the most desirable candidate for that sport (she tripped) she completed almost 800 competition miles with me. I went looking for endurance prospects after that, and I fell in love with them too. Which means, it’s possible to fall in love with a horse that can partner with you in what you enjoy doing.
years, I bought horses that could do what I was doing, endurance riding, though the first one was chosen because I just fell in love with her. I knew her and had been riding her for a year. Then we got into endurance riding. Even though she wasn’t the most desirable candidate for that sport (she tripped) she completed almost 800 competition miles with me. I went looking for endurance prospects after that, and I fell in love with them too. Which means, it’s possible to fall in love with a horse that can partner with you in what you enjoy doing. that may come up in your new journey.
that may come up in your new journey. It’s very common for horses to be afraid of bodywork, especially if they have received fear-based training or a number of unpleasant veterinary procedures. Of course, veterinary procedures and surgeries are often non-negotiable. When I have a procedure personally, I can only imagine what that feels like to the horse who doesn’t understand why it’s being done to him or her.
It’s very common for horses to be afraid of bodywork, especially if they have received fear-based training or a number of unpleasant veterinary procedures. Of course, veterinary procedures and surgeries are often non-negotiable. When I have a procedure personally, I can only imagine what that feels like to the horse who doesn’t understand why it’s being done to him or her.
 If your horse is continually miserable or reactive during a visit from any practitioner, it may be worthwhile to re-evaluate that professional relationship.
If your horse is continually miserable or reactive during a visit from any practitioner, it may be worthwhile to re-evaluate that professional relationship. Sometimes I find that the owner isn’t aware of what other professionals are doing with their horses.
Sometimes I find that the owner isn’t aware of what other professionals are doing with their horses.


 As my horse and I travel up the rise of the one track trail onto the mesa it feels and looks different somehow. Not just the weather has kept me away for a few months. Injuries, new horse training. All that went before falls away as we get to experience the lightness of steps and rhythm of the shift in terrain.
As my horse and I travel up the rise of the one track trail onto the mesa it feels and looks different somehow. Not just the weather has kept me away for a few months. Injuries, new horse training. All that went before falls away as we get to experience the lightness of steps and rhythm of the shift in terrain. I feel when I am riding this horse that we have known each other forever, before we ever met in person, before I ever slipped on his back. There is something amoebic about it, like a James Michener novel, a “knowing” from the beginning of time. It took no time at all to come together as person and horse, horse and rider. He was already trained but highly nervous in his response to life. A horse that made me feel good because it was apparent that it was all about the relationship and the relationship was easy from the beginning. We were what each other wanted and needed. It wasn’t one of those “relationship-building” challenges we hear so much about.
I feel when I am riding this horse that we have known each other forever, before we ever met in person, before I ever slipped on his back. There is something amoebic about it, like a James Michener novel, a “knowing” from the beginning of time. It took no time at all to come together as person and horse, horse and rider. He was already trained but highly nervous in his response to life. A horse that made me feel good because it was apparent that it was all about the relationship and the relationship was easy from the beginning. We were what each other wanted and needed. It wasn’t one of those “relationship-building” challenges we hear so much about.

 Red isn’t a replacement, she is her own horse. She is young and curious about everything, and especially her interactions with humans and her training. She loves her training. What I’m seeing in her is that everything is an adventure. While her first years were fraught with uncertainty, fear and mistreatment, when she didn’t want anyone to catch or touch her, she has now landed somewhere where everyone listens to her and she wants to listen.
Red isn’t a replacement, she is her own horse. She is young and curious about everything, and especially her interactions with humans and her training. She loves her training. What I’m seeing in her is that everything is an adventure. While her first years were fraught with uncertainty, fear and mistreatment, when she didn’t want anyone to catch or touch her, she has now landed somewhere where everyone listens to her and she wants to listen.




 A healing journey is specific, non-specific, historic, full of layers and wondrous avenues of enlightenment. The layers that developed first – en utero, at birth – will be deepest in the body, and the last ones to heal. Perhaps we can go farther back than that – generations that will heal last, if at all in this lifetime. The healing journey is one of seeking to unravel those layers in the body’s time, as it has a time of its own. Seeking self-correction.
A healing journey is specific, non-specific, historic, full of layers and wondrous avenues of enlightenment. The layers that developed first – en utero, at birth – will be deepest in the body, and the last ones to heal. Perhaps we can go farther back than that – generations that will heal last, if at all in this lifetime. The healing journey is one of seeking to unravel those layers in the body’s time, as it has a time of its own. Seeking self-correction. When I talk about injury, that injury could be internal or external, it could be musculoskeletal, visceral, neurological, circulatory, emotional, psychological, psychic…
When I talk about injury, that injury could be internal or external, it could be musculoskeletal, visceral, neurological, circulatory, emotional, psychological, psychic…
 Horses demonstrate to us repetitive stress in so many ways. They are subjected to repetitive activities – training, carrying people with unaddressed repetitive stress and compensatory patterns, saddles, bridles, other tack, trailering, abuse, repetitive behaviors.
Horses demonstrate to us repetitive stress in so many ways. They are subjected to repetitive activities – training, carrying people with unaddressed repetitive stress and compensatory patterns, saddles, bridles, other tack, trailering, abuse, repetitive behaviors. to take place slowly, addressing each layer as an individual, peeling them back as the body is able to address them.
to take place slowly, addressing each layer as an individual, peeling them back as the body is able to address them. it is those things, the compensation is coming from a lot of places and the body wants to be addressed as a whole. Not only will it show its compensation, it will show its strengths – where it can move and where it is light and receptive.
it is those things, the compensation is coming from a lot of places and the body wants to be addressed as a whole. Not only will it show its compensation, it will show its strengths – where it can move and where it is light and receptive.




 All of us – horse and human – hold tension in our bodies and we also have areas that just don’t speak. We have places that don’t work as well as others. My right leg can get funky in the hip socket, for example. I could sit up there and worry about what a terrible rider I am and I shouldn’t ride because I’m not always symmetrical and blah blah blah, but if I focus on all the dysfunction, then I am missing what my body can do, and how it can support the areas that aren’t working quite so well. My horse has stuff going on in her hips also. I focus on the healing available in her body. And guess what? Even though she has that stuff, she is a beautiful mover. I sit on her, and I feel each part of me and her, and focus on the parts that work really well while holding an awareness of what I’d like to have shift.
All of us – horse and human – hold tension in our bodies and we also have areas that just don’t speak. We have places that don’t work as well as others. My right leg can get funky in the hip socket, for example. I could sit up there and worry about what a terrible rider I am and I shouldn’t ride because I’m not always symmetrical and blah blah blah, but if I focus on all the dysfunction, then I am missing what my body can do, and how it can support the areas that aren’t working quite so well. My horse has stuff going on in her hips also. I focus on the healing available in her body. And guess what? Even though she has that stuff, she is a beautiful mover. I sit on her, and I feel each part of me and her, and focus on the parts that work really well while holding an awareness of what I’d like to have shift. Certainly, work can be done on some of these issues independently of the horse/rider relationship, and I do that in many cases where a person may need individual table work ahead of a horse/rider session, or the horse needs to receive an entire session on his own. If someone has major back trouble, I’m going to work on that, and same with the horse. But once the bodies are free of great inhibition, we can bring them together and see where they can strengthen and enhance each other, and bring space into the relationship that may have been restricted before.
Certainly, work can be done on some of these issues independently of the horse/rider relationship, and I do that in many cases where a person may need individual table work ahead of a horse/rider session, or the horse needs to receive an entire session on his own. If someone has major back trouble, I’m going to work on that, and same with the horse. But once the bodies are free of great inhibition, we can bring them together and see where they can strengthen and enhance each other, and bring space into the relationship that may have been restricted before. ways of beginning this work. While grooming your horse you can feel along the spine for any irregularities. If you don’t know anatomy, it’s helpful to get a simple equine anatomy book – and a human one while you’re at it! Learn where the bones are. Everything else is related to or attached to the bones in some way, so it’s a great place to start.
ways of beginning this work. While grooming your horse you can feel along the spine for any irregularities. If you don’t know anatomy, it’s helpful to get a simple equine anatomy book – and a human one while you’re at it! Learn where the bones are. Everything else is related to or attached to the bones in some way, so it’s a great place to start.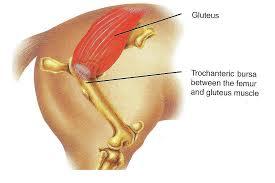
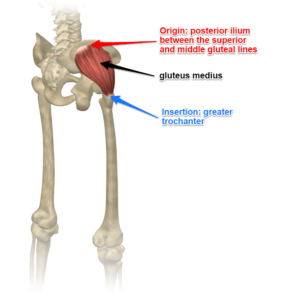
 After that I may do a little bit of bodywork on areas I see are not working so well on my horse, and stretch out myself. You can apply your own exercises, such as qi gong, yoga, Feldenkrais, etc. and in Ortho-Bionomy© we have a lot of self-care exercises for people and ones you can do for your horse. Some of them I have adapted to use in the saddle as well.
After that I may do a little bit of bodywork on areas I see are not working so well on my horse, and stretch out myself. You can apply your own exercises, such as qi gong, yoga, Feldenkrais, etc. and in Ortho-Bionomy© we have a lot of self-care exercises for people and ones you can do for your horse. Some of them I have adapted to use in the saddle as well. Much thought has been given over centuries to how to ride efficiently and so as to bring out the best in the horse and rider. With the Mounted Body Balance™ approach, an older horse can move better than he or she ever has and so can her rider. Life isn’t static so we can’t guarantee that any of us are not going to have some physical challenges, but there is a lot we can solve and make more comfortable with this type of work. A horse may be able to help you with your body issues without impairing his/her own stride or balance. Of course, aging will limit what you can do but why not try to do what you love comfortably for as long as you can? As a physical therapist friend of mine says, “I’m here to help you be able to do what you love for longer.”
Much thought has been given over centuries to how to ride efficiently and so as to bring out the best in the horse and rider. With the Mounted Body Balance™ approach, an older horse can move better than he or she ever has and so can her rider. Life isn’t static so we can’t guarantee that any of us are not going to have some physical challenges, but there is a lot we can solve and make more comfortable with this type of work. A horse may be able to help you with your body issues without impairing his/her own stride or balance. Of course, aging will limit what you can do but why not try to do what you love comfortably for as long as you can? As a physical therapist friend of mine says, “I’m here to help you be able to do what you love for longer.”