I entitled this “Getting a Horse” because horses come to us through different channels, not always through purchase or adoption. Whatever avenue they come through, getting a horse should be a thoughtful endeavor. There is no right way to do this, though It might be helpful to have a few guidelines, even if they get flung to the winds!
There are many checklists on what to look for when looking for a new horse, and they usually cite very sensible considerations. But many people have an emotional draw to a particular horse that doesn’t have much to do with common sense, but more to do with a sixth sense.
For  years, I bought horses that could do what I was doing, endurance riding, though the first one was chosen because I just fell in love with her. I knew her and had been riding her for a year. Then we got into endurance riding. Even though she wasn’t the most desirable candidate for that sport (she tripped) she completed almost 800 competition miles with me. I went looking for endurance prospects after that, and I fell in love with them too. Which means, it’s possible to fall in love with a horse that can partner with you in what you enjoy doing.
years, I bought horses that could do what I was doing, endurance riding, though the first one was chosen because I just fell in love with her. I knew her and had been riding her for a year. Then we got into endurance riding. Even though she wasn’t the most desirable candidate for that sport (she tripped) she completed almost 800 competition miles with me. I went looking for endurance prospects after that, and I fell in love with them too. Which means, it’s possible to fall in love with a horse that can partner with you in what you enjoy doing.
There are plenty of stories of horses overcoming physical and mental challenges in sports or as pleasure horses. I hear people say, I bought this horse because she was a palomino, I fell in love with this horse right away, I felt sorry for this horse, I thought I could give this horse a better life. Or, I just lost my horse and I’m looking for one different from him or just like him. And then sometimes a horse just saunters into your life and that’s it – an unexpected foal, a neighbor can’t take their horse with them….
All of these are valid reasons as long as you are willing to put in the time and energy on your passion.
And, as the new owner, you need to be prepared for what may come down the road. If you want a horse just to love, and you don’t mind that the horse is on and off lame, or you’re a bodyworker or other therapist and you feel you can make a difference, then that will probably be a good match.
If you want to do a fast or challenging sport, then this wouldn’t be the best horse for you.
The more clear you are about what you’re looking for, the more successful you will be. When I hear, I don’t care what age or what the horse looks like, or what breed, it’s more difficult to make a good choice. Will you ultimately get frustrated if your horse can’t do what you dream of doing?
Eventually they all will grow old and not be able to join you on your wild adventures, but maybe you want them to start out in the adventure category, even if it’s just for a simple ride out from the barn.
Shelters are full of horses that are adopted into what they think are forever homes, only to be returned because they don’t measure up. Many shelters have a good sense of who is going to be a good owner for their horses. Yet, new owners have high expectations and not all know how to give the animal the time it takes to adjust, and to get to know their new horse. Some horses just go with the flow and fit in easily. And others need time to adjust. They may not like something about their life.
Some horses have been rescued from some unimaginable neglect or cruelty. They don’t necessarily know how to behave around other horses or can be afraid of strangers. For you the new owner, it’s like taking on a foster child. Some horses fit in and are eternally grateful. A big part of their healing can come from a new home with all they need, and the space to figure out where they are, the other horses and animals in their yard, the different sights and smells.
For many people, the objective of getting the rescue is they are very affordable, the vetting and assessment has already been done, and hopefully, someone has determined the riding level needed for that horse. Because these organizations rely largely on volunteers whom they train from the ground up, plus paid vets and farriers, the horses can have good contact with humans. There are many success stories with these organizations, which is wonderful, but there are many horses returned because they don’t fit the new owners’ vision or fit in with existing pasture mates.
Horses coming from auctions or kill pens can present other problems that are not in their descriptions.
My checklist includes some other considerations:
- Have someone knowledgeable check their conformation. Conformation is important because it doesn’t make sense to expect a horse to achieve certain goals with bad conformation, although some horses have been known to overcome poor conformation. Still, the body doesn’t lie. Weak pasterns or hindquarters, or a swayback can be painful for a horse and make riding unpleasant for them.
- Have a farrier, preferably your own, check the horse’s feet.
- Have your vet check your horse’s teeth, to identify age as well as condition.
- If you work with a horse trainer or bodyworker, their opinions could be helpful.
- Check to see how your horse rolls – does he or she get up and down easily?
- Get a lameness exam.
- Feel along the spine to see if the horse has any soreness, or get a bodyworker to assess that and the entire body that way.
- Note the horse’s demeanor – is he or she curious or shut down? A number of horses are shut down and come from all walks of life – high performance, low performance, rescues, horses who have been alone for a long time.
- Find out the horse’s social habits and preferences – does this horse get along with other horses, does he eat all the food when in a group, is he particularly studdy with mares, etc.?
- Size – is the horse the right size for your body and physical capabilities?
- Do you have the necessary riding and/or horsemanship skills for the horse?
- Observe coat, posture, facial expression, eyes, demeanor, leg straightness and stance.
- How does the horse make you feel?
- Do you already know the horse?
- How does the horse connect with you?
- Do you feel you are making this decision with a clear heart?
This last one is perhaps most important, because you need the life force for some of the things that may come up in your new journey.
that may come up in your new journey.
Once you’ve checked out all these things or those that are pertinent, in addition to the usual health checkups, take stock of your own capabilities and expectations. Are these problems I can solve or do they feel like I’m on overwhelm?
What kind of outside help can I get, or do I need, to support this horse and myself?
It’s much easier to make a good decision before you bring your new horse home. Years ago, someone I knew bought a coon-footed horse with possible ringbone from a reputable breeder. It was immediately obvious to me that the horse would have problems with soundness throughout its life, even though at the onset, he was sound. The new owner was madly in love with this horse and kept him throughout his life, spent thousands of dollars which seem irrelevant when you want to make your horse well, and nursed him through one disappointing veterinary catastrophe after another.
This horse was fortunate to end up with such an owner, as many people would send the horse on to an uncertain future.
Because horses aren’t cheap to keep, this can often end someone’s aspiration of going on to do great things in a particular sport. Or it can be life changing in other ways: send the owner off in an exploration of how to help their horse get better and learn a lot in the process.
Another example is a rescue mare who is beautifully built and very pretty, but has so much pain in her body she doesn’t enjoy riding. She has been adopted out a few times and comes back because she charges at her handler in the round pen and won’t stand for mounting. This mare could have an ulcer, musculoskeletal or other physical problems making her really unhappy. Can this pain be reduced to a manageable level so her behavioral problems can diminish and she can enjoy life?
There is a flow to all of this and if you get into the flow and recognize what your heart’s desire is and what you want to and can do, then it will probably work out okay. There are more people these days who want a horse to care for, to provide something special for, than ever before. There are those with good skills who realize they can help a certain horse flourish, so they take on that horse, rather than go buy one that already has training.
The journey you embark on will have its own qualities and shape you and your new horse! In every horse, there is a gem waiting to be burnished. Some horses from the worst beginnings can become your best life partners, and make you forever glad you took the chance on them.




 It’s very common for horses to be afraid of bodywork, especially if they have received fear-based training or a number of unpleasant veterinary procedures. Of course, veterinary procedures and surgeries are often non-negotiable. When I have a procedure personally, I can only imagine what that feels like to the horse who doesn’t understand why it’s being done to him or her.
It’s very common for horses to be afraid of bodywork, especially if they have received fear-based training or a number of unpleasant veterinary procedures. Of course, veterinary procedures and surgeries are often non-negotiable. When I have a procedure personally, I can only imagine what that feels like to the horse who doesn’t understand why it’s being done to him or her.
 If your horse is continually miserable or reactive during a visit from any practitioner, it may be worthwhile to re-evaluate that professional relationship.
If your horse is continually miserable or reactive during a visit from any practitioner, it may be worthwhile to re-evaluate that professional relationship. Sometimes I find that the owner isn’t aware of what other professionals are doing with their horses.
Sometimes I find that the owner isn’t aware of what other professionals are doing with their horses.

 Years ago, when I was riding endurance, many rider/horse teams would head to El Paso during the winter months to ride. Horses had not had much riding time in the colder climates so one had to be careful as they traveled in the deep desert sand. Often the injuries that went unnoticed from the winter riding would appear in the spring.
Years ago, when I was riding endurance, many rider/horse teams would head to El Paso during the winter months to ride. Horses had not had much riding time in the colder climates so one had to be careful as they traveled in the deep desert sand. Often the injuries that went unnoticed from the winter riding would appear in the spring.
 ve around freely is different than the measured, focused exercise we ask of a horse in daily work. Both are very important.
ve around freely is different than the measured, focused exercise we ask of a horse in daily work. Both are very important. Walking on different types of terrain for horses who can manage it is vital.
Walking on different types of terrain for horses who can manage it is vital. comfortable being ridden anymore. He’s now 26. He enjoys walks and arena activities. He is also teaching our young mare Red to be more curious than she already is. I think this is an excellent way for him to spend his golden years.
comfortable being ridden anymore. He’s now 26. He enjoys walks and arena activities. He is also teaching our young mare Red to be more curious than she already is. I think this is an excellent way for him to spend his golden years.



 These are horses who have no relationship with their riders. They are ridden by many different riders in preparation for this event and considered “schoolmasters.” But to go through an event at this high level of stress, they need the relationship. When things get scary it’s not enough to simply know how to ride, you need to know the way that animal thinks, moves, it’s preferences, what frightens it, know it deep down so that you can set up the best possible outcome. If introducing a horse to new things, it’s best if he has a familiar, much loved person to help him or her through it all.
These are horses who have no relationship with their riders. They are ridden by many different riders in preparation for this event and considered “schoolmasters.” But to go through an event at this high level of stress, they need the relationship. When things get scary it’s not enough to simply know how to ride, you need to know the way that animal thinks, moves, it’s preferences, what frightens it, know it deep down so that you can set up the best possible outcome. If introducing a horse to new things, it’s best if he has a familiar, much loved person to help him or her through it all. addle, not a short stint in an Olympic arena that involves maybe 5-10 minutes of connection! Plus the stress level is way down on the meter. We were riding to win a t-shirt, not an Olympic gold medal.
addle, not a short stint in an Olympic arena that involves maybe 5-10 minutes of connection! Plus the stress level is way down on the meter. We were riding to win a t-shirt, not an Olympic gold medal.


 All of us – horse and human – hold tension in our bodies and we also have areas that just don’t speak. We have places that don’t work as well as others. My right leg can get funky in the hip socket, for example. I could sit up there and worry about what a terrible rider I am and I shouldn’t ride because I’m not always symmetrical and blah blah blah, but if I focus on all the dysfunction, then I am missing what my body can do, and how it can support the areas that aren’t working quite so well. My horse has stuff going on in her hips also. I focus on the healing available in her body. And guess what? Even though she has that stuff, she is a beautiful mover. I sit on her, and I feel each part of me and her, and focus on the parts that work really well while holding an awareness of what I’d like to have shift.
All of us – horse and human – hold tension in our bodies and we also have areas that just don’t speak. We have places that don’t work as well as others. My right leg can get funky in the hip socket, for example. I could sit up there and worry about what a terrible rider I am and I shouldn’t ride because I’m not always symmetrical and blah blah blah, but if I focus on all the dysfunction, then I am missing what my body can do, and how it can support the areas that aren’t working quite so well. My horse has stuff going on in her hips also. I focus on the healing available in her body. And guess what? Even though she has that stuff, she is a beautiful mover. I sit on her, and I feel each part of me and her, and focus on the parts that work really well while holding an awareness of what I’d like to have shift. With Ortho-Bionomy© for both horse and rider, we can learn what is holding up the bus. Riding instructors have wonderful ways of encouraging the horse forward, ways for riders’ to hold their legs so that the legs are not being counterproductive for the horse, or to sit correctly so as not to impede the horse’s movement – all of that has to do with the anatomy and the relationship of the two bodies working in sync, or not.
With Ortho-Bionomy© for both horse and rider, we can learn what is holding up the bus. Riding instructors have wonderful ways of encouraging the horse forward, ways for riders’ to hold their legs so that the legs are not being counterproductive for the horse, or to sit correctly so as not to impede the horse’s movement – all of that has to do with the anatomy and the relationship of the two bodies working in sync, or not.
 Certainly, work can be done on some of these issues independently of the horse/rider relationship, and I do that in many cases where a person may need individual table work ahead of a horse/rider session, or the horse needs to receive an entire session on his own. If someone has major back trouble, I’m going to work on that, and same with the horse. But once the bodies are free of great inhibition, we can bring them together and see where they can strengthen and enhance each other, and bring space into the relationship that may have been restricted before.
Certainly, work can be done on some of these issues independently of the horse/rider relationship, and I do that in many cases where a person may need individual table work ahead of a horse/rider session, or the horse needs to receive an entire session on his own. If someone has major back trouble, I’m going to work on that, and same with the horse. But once the bodies are free of great inhibition, we can bring them together and see where they can strengthen and enhance each other, and bring space into the relationship that may have been restricted before. ways of beginning this work. While grooming your horse you can feel along the spine for any irregularities. If you don’t know anatomy, it’s helpful to get a simple equine anatomy book – and a human one while you’re at it! Learn where the bones are. Everything else is related to or attached to the bones in some way, so it’s a great place to start.
ways of beginning this work. While grooming your horse you can feel along the spine for any irregularities. If you don’t know anatomy, it’s helpful to get a simple equine anatomy book – and a human one while you’re at it! Learn where the bones are. Everything else is related to or attached to the bones in some way, so it’s a great place to start.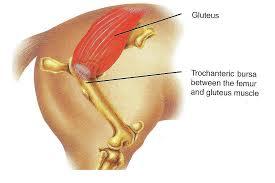
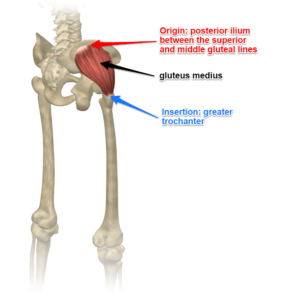
 After that I may do a little bit of bodywork on areas I see are not working so well on my horse, and stretch out myself. You can apply your own exercises, such as qi gong, yoga, Feldenkrais, etc. and in Ortho-Bionomy© we have a lot of self-care exercises for people and ones you can do for your horse. Some of them I have adapted to use in the saddle as well.
After that I may do a little bit of bodywork on areas I see are not working so well on my horse, and stretch out myself. You can apply your own exercises, such as qi gong, yoga, Feldenkrais, etc. and in Ortho-Bionomy© we have a lot of self-care exercises for people and ones you can do for your horse. Some of them I have adapted to use in the saddle as well. Much thought has been given over centuries to how to ride efficiently and so as to bring out the best in the horse and rider. With the Mounted Body Balance™ approach, an older horse can move better than he or she ever has and so can her rider. Life isn’t static so we can’t guarantee that any of us are not going to have some physical challenges, but there is a lot we can solve and make more comfortable with this type of work. A horse may be able to help you with your body issues without impairing his/her own stride or balance. Of course, aging will limit what you can do but why not try to do what you love comfortably for as long as you can? As a physical therapist friend of mine says, “I’m here to help you be able to do what you love for longer.”
Much thought has been given over centuries to how to ride efficiently and so as to bring out the best in the horse and rider. With the Mounted Body Balance™ approach, an older horse can move better than he or she ever has and so can her rider. Life isn’t static so we can’t guarantee that any of us are not going to have some physical challenges, but there is a lot we can solve and make more comfortable with this type of work. A horse may be able to help you with your body issues without impairing his/her own stride or balance. Of course, aging will limit what you can do but why not try to do what you love comfortably for as long as you can? As a physical therapist friend of mine says, “I’m here to help you be able to do what you love for longer.”





